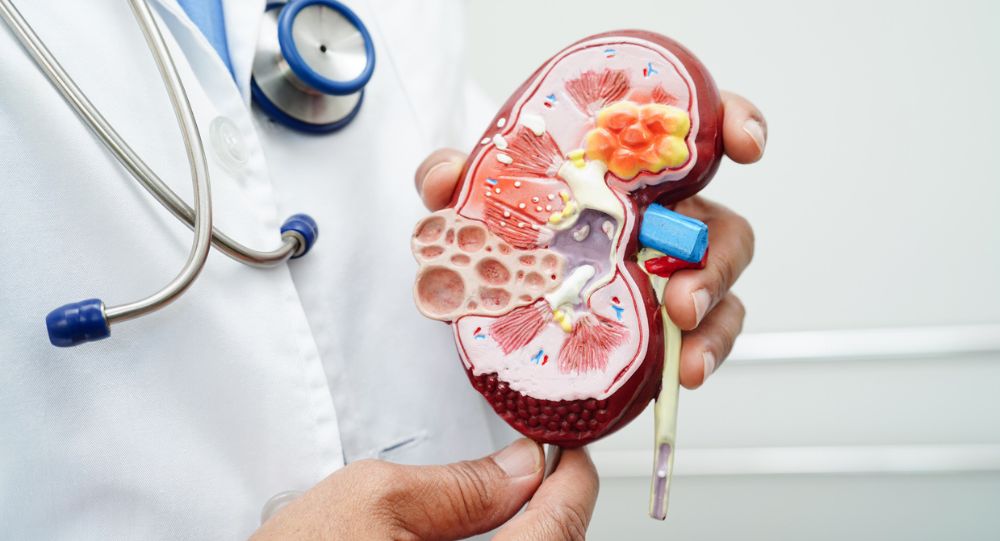
Pyelonephritis, commonly known as a kidney infection, is a type of urinary tract infection (UTI) that often begins in the bladder and moves up to one or both kidneys. If left untreated, a kidney infection may lead to severe health complications. Fortunately, most kidney infections can be treated with antibiotics. However, it does require urgent medical attention.
However, there are several things you may do to help prevent a kidney infection from developing in the first place. Prevention often begins with identifying the causes of a kidney infection and working to avoid them.
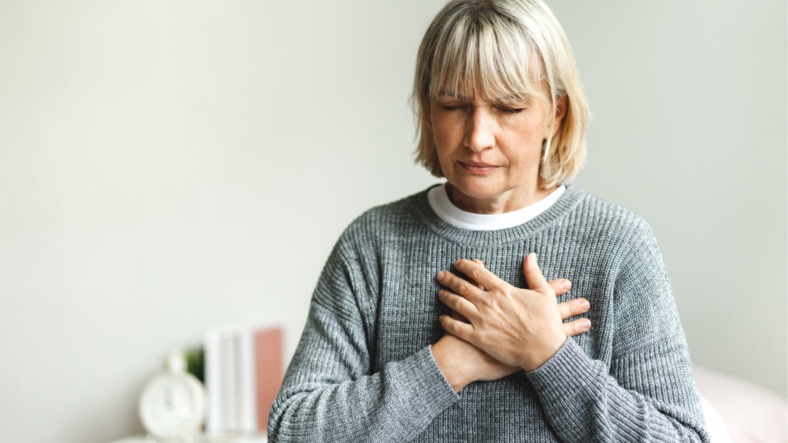
Symptoms of a Kidney Infection
If you begin to notice any of the following symptoms of a kidney infection, it is imperative to make an appointment with a kidney specialist immediately.
- Flank pain
- Chills
- Fever
- Nausea or vomiting
- Frequent urination
- Pain or a burning sensation when urinating
- Pain in your back, side, groin, or abdomen
- Bloody or cloudy urine
- Foul-smelling urine
How is a Kidney Infection Diagnosed?
Kidney infections are often diagnosed through a urine sample, which tests for bacteria, blood or pus in the urine. Additionally, a blood sample for a culture test may be taken. A culture is a test that checks for bacteria and other organisms in the blood. Imaging tests, such as an ultrasound, CT scan, or a special type of X-ray called a voiding cystourethrogram, may also be ordered.
A voiding cystourethrogram uses contrast dye to help doctors see the structure of the urinary tract. The test involves injecting a contrast dye into the bladder through a small tube and taking X-rays as the patient urinates. This helps identify any blockages or other abnormalities in the urinary tract.
What Causes Kidney Infections?
Kidney infections are most commonly caused by bacteria entering the urethra and traveling up to the bladder. From there, the bacteria can move into the kidneys. A kidney infection may also occur from a blockage in the urinary tract, such as a kidney stone.
Risk Factors for Kidney Infections
There are several factors that may significantly increase the chances of developing an infection of the kidneys. If you fall into any of the following categories, you may be at a higher risk for pyelonephritis and will need to take extra care to prevent an infection. Common risk factors for kidney infections include:
Being Female
Women have shorter urethras than men making it easier for bacteria to travel from the urethra to the bladder. Once bacteria enter the bladder, they can move up to the kidneys and cause an infection. Additionally, pregnant women are at a higher risk of developing a kidney infection. This is due to the fact that pregnancy puts extra pressure on the bladder and may interfere with the flow of urine. When urine becomes stagnant, it creates an environment where bacteria can thrive, causing an infection.
Having a Weakened Immune System
If you have a weakened immune system due to a chronic illness or certain medical treatments, you may be at a higher risk of developing pyelonephritis. This is because your body may not be able to fight off bacteria as effectively. Diseases such as HIV or cancer and treatments such as chemotherapy may weaken your immune system making you more susceptible to pyelonephritis.
Nerve or Spinal Cord Damage
If you damage your nerves or spinal cord, you may be at a higher risk of developing a kidney infection. Having nerve or spinal cord damage may make it difficult to identify the physical symptoms of a kidney infection. Early treatment is essential to prevent serious complications. However, for those with nerve or spinal cord damage, detecting an infection may be challenging.
Urinary Tract Obstruction
Whether it be a narrowed urethra, kidney stone, or an enlarged prostate, any obstruction in the urinary tract may increase your risk of developing a kidney infection. This is because an obstruction prevents urine from flowing properly and makes it harder to empty your bladder. Therefore, allowing bacteria to build up and increase your risk of infection.
Tips to Help Prevent Kidney Infections
Even if you are at a higher risk for developing pyelonephritis, there are several things you can do to help prevent it. The best way to avoid a kidney infection is to practice good hygiene and take care of your urinary tract. Other ways to avoid a kidney infection include:
Drink Plenty of Water
Water helps to flush out bacteria and other toxins from your body when you urinate. Drinking at least eight glasses of water a day may prevent bacteria from building up in your urinary tract and causing an infection. Furthermore, staying well hydrated may reduce your risk of developing a kidney stone, which may cause a urinary tract obstruction.
Don’t Hold in Your Pee
Holding your urine in for too long may cause your bladder muscles to weaken and make it difficult to empty your bladder completely. When urine is left in the bladder, it provides a breeding ground for bacteria to grow. This increases your risk of developing a urinary tract infection, which may lead to pyelonephritis. That being said, it is vital to empty your bladder as soon as you feel the urge to go.
Urinate After Sexual Intercourse
Sexual intercourse may introduce bacteria into the urinary tract. In order to flush out any bacteria that may have entered, it is important to urinate as soon as you can after sex. When you urinate, bacteria trying to enter the bladder will be flushed out before it has a chance to travel up the urethra and cause a UTI.
Receive World-class Renal Care at the Kidney and Hypertension Center
The Kidney and Hypertension Center (KHC) is dedicated to providing world-class renal care. We offer a variety of services for those with kidney conditions and hypertension. In addition to providing patients with the best possible care, we also offer educational resources to help patients better understand their condition. Request an appointment today to learn more about how we can help you optimize your kidney function and prevent infections.